link to repo
link to project site
In this project I made a setence generator in which you can input your own pragraph and using the markov procces it will generate a sentence. A markov chain is a model in which you can predict future outcomes based on the thing that came before it and is used for sequential data.
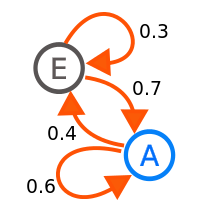
The image of above is a markov chain a visual of a very simple markov chain. As you can see Point E is more likely to go to Point A, but Point A is just slightly more likely to go back to it’s self. A real life example of this is the weather. Using a markov chain you can predict what the weather will be given the weather before. If we create a visual representation for the weather a simple visual would look like this.
C S S S S S S S C C R R C S S S S C S
In the daigram above R represents rain, S represents sun and C represents cloudy and every letter represents a day in which that was the weather. As you can see this is sequential data so it works perfect for what we are trying to do. Now For every sunny day it will almost always go back to sunny but in the case that it doesnt it wiill go to cloudy that is becuase the probability is much higher for sunny to go back to sunn than sunny to cloudy, altough still possible its just less likely. This is a simple markov chain and what it can be used for
Now to how I created a markov chain in python to create a sentence, this is
how i went about it. First we need our data so I first statrted with using a
bible from the internet to use as our data and called it bible.txt. Once I had a sample bool I created a python file called sentence-gen.py. In there is where I put all my functions. From there
I opened the book cleaned the data with some regular expresions and put the book into the list which I wont explain because it’s pretty straight forward and can be found in the project repo. Now to create our actual markov chain in which we would generate our sentence from it looked like this.
def create_dict(tokens, tokens_index):
"""
This function takes in a list of tokens
and creates a dictionary to with a word as its
key and the words after it as its value.
"""
words_with_nearby = {}
for token in tokens_index:
words_with_nearby[token] = []
for i in range(len(tokens) - 1):
current_word = tokens[i]
next_word = tokens[i + 1]
words_with_nearby[current_word].append(next_word)
return create_sentence(**words_with_nearby)
First we have a tokens which is a list of all the words, and tokens_index
which is a list of all the words without duplicates. We then creat a
dictionary with the populating the keys with the our tokens, once thats over
we add the values and we do that by looping through our tokens then we get
words and the words after that. That will be our chain. Altough we dont
have probalities like an actual markov chain. This is a simple markov chain
that works. Another thing I wanted to metion was that this
markov chain uses unigrams which look like this
#this is a unigram which is used in the project
#a unigram stores one value
unigram = {'let': ['there'], 'the': ['earth', 'face', 'deep', 'spirit', 'face', 'waters'], 'light': ['and'], 'moved': ['upon'], 'earth': ['was'], 'void': ['and'], 'darkness': ['was'], 'of': ['the', 'god', 'the'], 'was': ['without', 'upon', 'light'], 'god': ['moved', 'said'], 'there': ['be', 'was'], 'said': ['let'], 'deep': ['and'], 'and': ['the', 'void', 'darkness', 'the', 'god', 'there'], 'face': ['of', 'of'], 'spirit': ['of'], 'upon': ['the', 'the'], 'waters': ['and'], 'without': ['form'], 'form': ['and'], 'be': ['light']}
Altough this works if we would want to create better sounding< sentences we would use bigrams which look like this.
#this is a bigram and could make better sounding setencees
#bigram stores two values
bigram = {'let there': ['be light'], 'the earth': ['was on'], 'be light': ['ther was']}:
But now the problem with using birgrams or trigrams etc. is that our setnece being generated would sound much more like the text we are sampling from and it would some even more alike if the text is a small page or two. Another thing I would like to mention is that no matter what text or book is being used the output would always be different from each other. Let’s take Yoda from Star Wars as an example, if we were to input a qoute like “Named must your fear be before banish it you can”, and then input some like this as well “You must name your fear before you can banish it”. As you can see these quotes are very similar but in the markov chain that does not matter. The markov chain will see that in the first quote the probability of the word “be” is more likely to come after the word ” fear” as in the second qoute “before” is more likely to apear after the word fear, therefore creating different outputs
In the end, I’ve learned a lot from creating this project and creating reasearching what markov chains are and what they are used for. Doing this project I learned about the many uses it can have and how it can be used at higher levels to see future outcomes of certain data.
Output/Genrated Sentence:
the man should be laid waste it came and hasteth
Possible Improvements:
As of now my markov chain is not as complex as others, some possible improvements could be, using brigrams to create better sounding sentences altough I went over some downsides of that earlier such as sampled text would sound more like original text. Another possible improvement could be adding probabilites to each occuring word. This way we could select words on their probabilites instead of randomly selecting probabble words, which would also make better sounding sentences. Lastly I could turn this into a machine learning projects, which I dont know so much of yet but the idea would be that the computer would take in the text and as well look at the words an probabilities of them showing up and from learning patterns of the text provided it would create sentences. These are three possible ways this project could be improved to create a better markov chain that works more efficient and creates better sounding sentenecs.
